Black hole

Black hole, cosmic body with extremely intense gravity, of which nothing, even light, cannot escape. A black hole can form as a result of the death of a massive star. When such a star runs out of internal fusion fuels in its core at the end of its life, the nucleus becomes unstable and gravitationally collapses inward, and the outer layers of the star are blown away. The crushing mass of component matter falling from all sides compresses the dying star to a point of zero volume and infinite density called singularity.
Details of the structure of the black hole are calculated by Albert Einstein in "General Relativity. The singularity is at the center of the black hole and hidden in the object's surface. In the event horizon, the escape velocity (tj. the speed required for matter to escape from the gravitational field of a space object) exceeds the speed of light, so that even rays of light cannot escape into space. The event horizon radius is called the Schwarzschild Ray, after the German astronomer Karl Schwarzschild, which in 1916 year predicted the existence of collapsed star bodies, that do not emit radiation. The size of the Schwarzschild radius is proportional to the mass of the collapsing star. For a black hole with a mass of 10 times greater than the mass of the sun, the radius would be 30 Km (18,6 one thousand).
Only the most massive stars – those having more than three solar masses – they become black holes at the end of their lives. Less mass stars evolve into less compressed bodies, white dwarfs or neutron stars.
Black holes are usually not directly observable due to both their small size, as for that, that they do not emit light. However, they can be "observed" by the influence of their enormous gravitational fields on nearby matter. E.g, if the black hole is a member of the binary star system , matter flowing into it from its companion becomes intensely heated, and then emits copiously x-rays, before it enters the black hole's event horizon and disappears forever. One of the constituent stars of the Cygnus X-1 double X-ray system is a black hole. Outdoor in 1971 year in the constellation Cygnus, this binary consists of a blue supergiant and an invisible mass companion 14,8 times the mass of the sun, which revolve around each other in the period 5,6 day.
Some black holes are apparently of non-stellar origin. Various astronomers speculated, that large amounts of interstellar gas accumulate and collapse super massive black holes at the centers of quasars and galaxies. Is estimated, that the mass of gas falling rapidly into the black hole exudes over 100 times more energy, than is released by the same mass by nuclear fusion. Therefore, if millions or billions of solar masses of interstellar gas collapse into a large black hole under the influence of gravity, it would be responsible for the enormous energy production of quasars and some galactic systems..
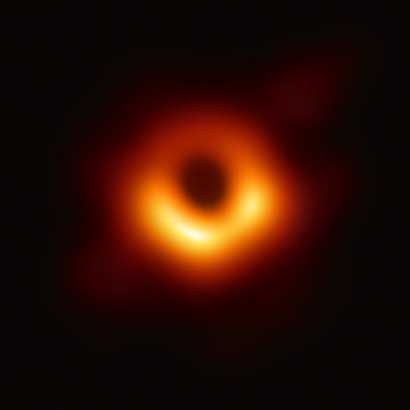
One such supermassive black hole, Sagittarius A * , is located in the center of the Milky Way. Observations of stars orbiting Sagittarius A. * show the presence of a black hole with a mass equivalent to over 4 000 000 sun. (For these observations, the American astronomer Andrea Ghez and the German astronomer Reinhard Genzel won the Nobel Prize in Physics at 2020 year) Supermassive black holes have also been detected in other galaxies. W 2017 On year, the Event Horizon Telescope acquired an image of a supermassive black hole at the center of Galaxy M87 . This black hole has a mass of six and a half billion suns, but only has 38 billion km (24 billion mil) diameter. It was the first black hole, which has been imaged directly. About the existence of even bigger black holes, each of which has an equal mass 10 billions of suns, can be deduced from the energy effects of the gas swirling at extremely high velocities around the center of the NGC 3842 the NGC 4889, galaxies near the Milky Way.
The existence of a different type of non-star black hole was proposed by British astrophysicist Stephen Hawking. According to Hawking's theory, lots of tiny primordial black holes, possibly less than or equal to the asteroid, could have arisen during the Big Bang, state of extremely high temperatures and densities, in which the universe arose 13,8 a billion years ago. These so-called. mini black holes, as well as a more massive variety, they lose mass over time under the influence of Hawking radiation and disappear. If certain theories of the universe, which require additional dimensions, They are correct, The Large Hadron Collider can produce a significant number of mini black holes.