What is the speed of light
What is the speed of light
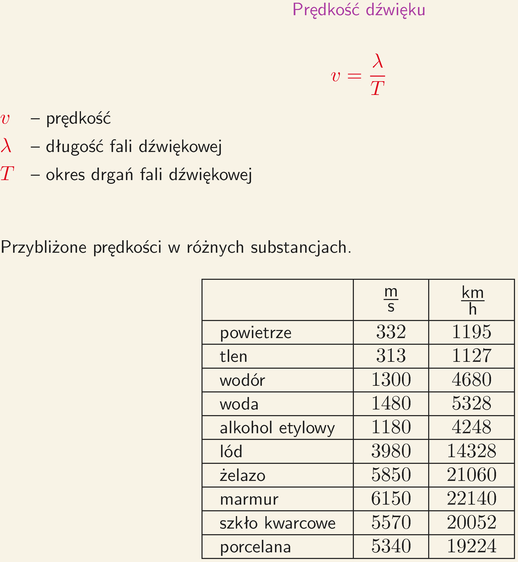
We often talk about the speed of light, so it is not a foreign term for anyone. We even use it in everyday language, if we want to say, that someone or something was moving extremely fast.
The speed of light is the most important constant in physics. It is given as the symbol "c". In short, it is the speed at which electromagnetic waves travel in a vacuum. It is the greatest known to us, possible speed of information or energy transfer. In the SI system, that is, in the international system of units of measurement, it is associated with magnetic permeability and constant dialectical, which are constants of nature.
The first measurements of the speed of light are not, as it might seem related to the science of the 20th century. Already in the 17th century, more precisely 1673 year, Danish astronomer Ole Roemer, as a result of his astronomical observations, tried to measure the speed of light. He was interested in the irregularity in the eclipses of Jupiter's moons, and he concluded, that this is due to the difference that light travels on the Jupiter-Earth path. The value he gave was c = 215000 km/s.
Other scientists also made further attempts to measure the speed of light. James Bradley, english scientist, measured the speed by the abberation test method, while Fizeau in 1849. made the first light measurement in the laboratory. Bradley's speed was c = 303000 km/s, Fizeau’a c=299860 km/s. Currently, the calculated speed of light is c = 299793 m / s .